Installing Docker on Fedora¶
To install Docker, you need the 64-bit version of one of these Fedora versions:
28
29
First, uninstall any older version of Docker using the following command:
sudo dnf remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-selinux \
docker-engine-selinux \
docker-engine
The recommended approach of installing Docker CE by setting up Docker’s repositories has been described here. For other approaches, please refer to Docker Docs.
Set up the repository¶
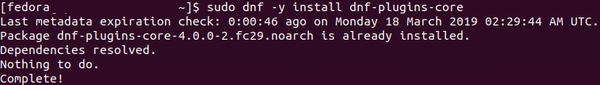
First, install the dnf-plugins-core package:
sudo dnf -y install dnf-plugins-core
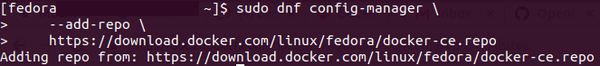
Next, set up the stable repository:
sudo dnf config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/fedora/docker-ce.repo
Install Docker-CE¶
Install the latest version of Docker CE using the following command:
sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Press y when prompted. If prompted to accept the GPG key, verify that the fingerprint matches 060A 61C5 1B55 8A7F 742B 77AA C52F EB6B 621E 9F35, and if so, accept it.
Now, start docker using the following command:
sudo systemctl start docker
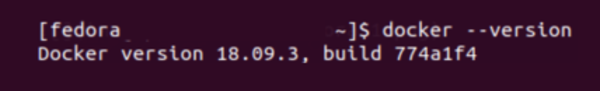
To verify that Docker has been installed succesfully, check the Docker version.
docker --version
The output on terminal should be similar to this:
Docker version 18.09.3, build 774a1f4
Install Docker Compose¶
To install Docker Compose, download the current stable release (1.24.0-rc1).
sudo curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.24.0-rc1/docker-compose-`uname -s`-`uname -m` -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Next, apply executable permissions to the binary.
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Installing Docker on Ubuntu¶
To install Docker CE, you need the 64-bit version of one of these versions:
Cosmic 18.10
Bionic 18.04 (LTS)
Xenial 16.04 (LTS)
First, uninstall the older docker versions (if any).
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
The recommended approach of installing Docker CE by setting up Docker’s repositories has been described here. For other approaches, please refer to Docker Docs.
Set up the repository¶
First, update the apt package index:
sudo apt-get update
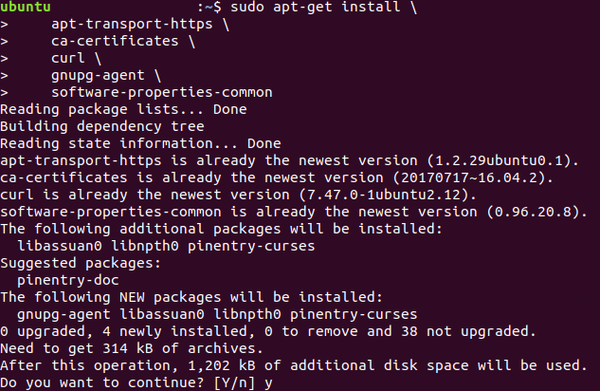
Install packages to allow apt to use a repository over HTTPS:
sudo apt-get install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg-agent \
software-properties-common
Press y when prompted.
Add Docker’s official GPG key:
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
Next, set up the stable repository:
sudo add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable"
Install Docker-CE¶
First, update the apt package index.
sudo apt-get update
Next, install the latest version of Docker CE.
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
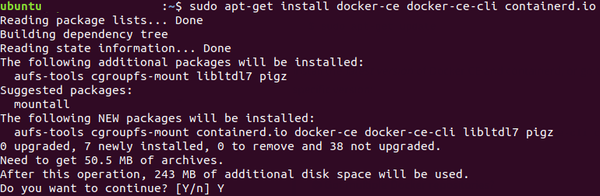
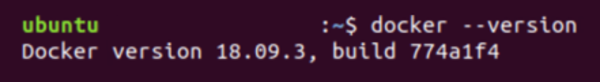
To verify that Docker has been installed succesfully, check the Docker version.
docker --version
The output on terminal should be similar to this:
Docker version 18.09.3, build 774a1f4
Install Docker Compose¶
To install Docker Compose, download the current stable release (1.24.0-rc1).
sudo curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.24.0-rc1/docker-compose-`uname -s`-`uname -m` -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose

Next, apply executable permissions to the binary.
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
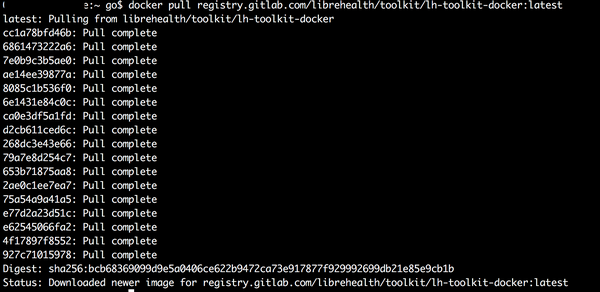
Pulling the container image¶
To run containers pull the container image:
You should see the similar console output:
Navigate to the directory where you cloned this project. Depending on how you want to interact with the container, run it in foreground or as a daemon.
Ensure that you do not have any other servers running on 8080 (tomcat) and 3306 (mysql).
To run the container in the foreground:
docker-compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml up
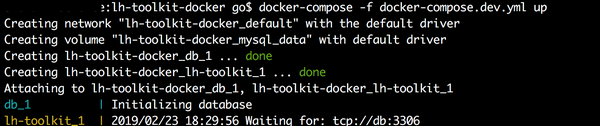
MySQL will be started first and then LH Toolkit will be started on the containers.
When you are done using LH Toolkit you can press Ctrl+C to stop the container.
To run the container in the background:
docker-compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml up -d
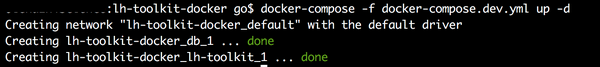
Using LH Toolkit¶
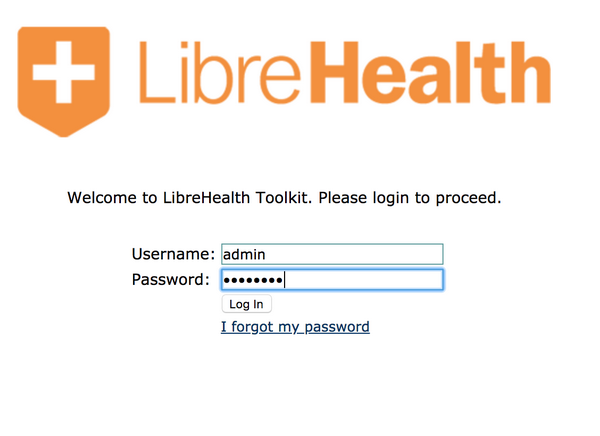
To start using LH Toolkit, point your browser to localhost:8080/lh-toolkit . The following are the authentication information:
User: admin
Pass: Admin123
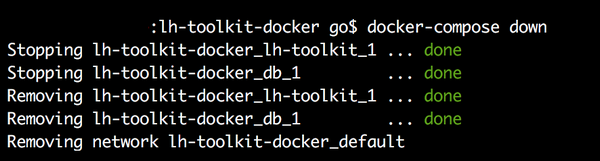
Bringing container down¶
To bring the container down and to free space on your machine run:
docker-compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml down
Troubleshooting¶
When you are pulling the container image, the directory you are in does not matter. However, if you try to run this docker image from outside of this project directory, you will get the following error:
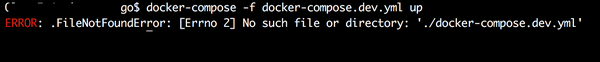
Navigate to the project directory and enter the command again.