Installing Docker on Windows 10¶
Docker is a computer program that performs operating-system-level virtualization, also known as “containerization”. Docker allows you to install software quickly and without worrying about dependencies. To use Docker images of software, you need to have Docker installed on your machine.
To check if you have Docker, run the terminal: click the “Start >> Program Files >> Accessories >> Command Prompt” to open a Command Prompt session using just your mouse. Click the “Start” button and type “cmd.” Right-click “Cmd,” select “Run as Administrator” and click “Yes” to open Command Prompt with elevated privileges.
Type in the terminal:
docker -v
If you do not see the version as an output, you need to install Docker. Most modern computes can run Docker, if you have any doubts, please check the official documentation.
Downloading and installing Docker¶
Please visit the official page of Docker Desktop for Windows and click the Download button.
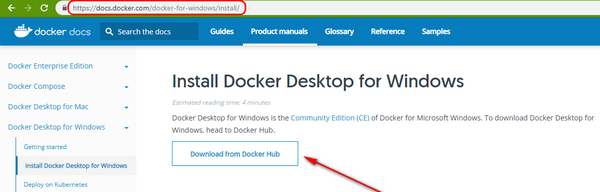
You will be redirected to Dockerhub. You need to register and login to download the installation file.
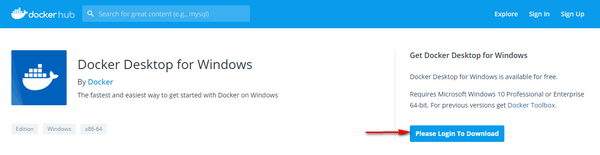
The registration process is very simple and straightforward. After registering, enter you login and password.
You will be redirected to Dockerhub. Now the download button will be enabled.
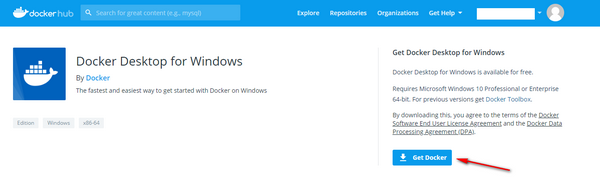
Navigate to the directory where you saved the installation file. Double click the installation file.
Accept the defaults.
The installation will continue.
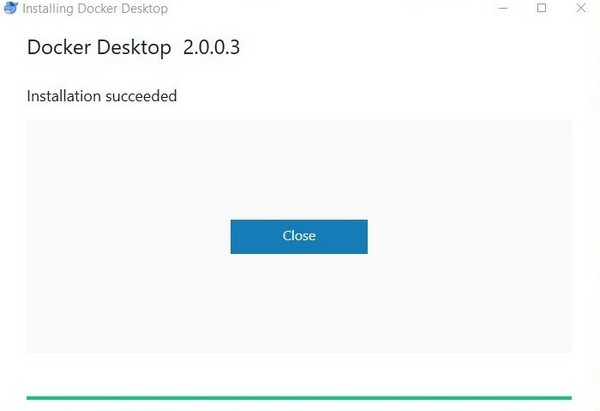
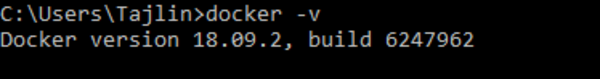
Open the terminal and type:
docker -v
You should see the similar output.
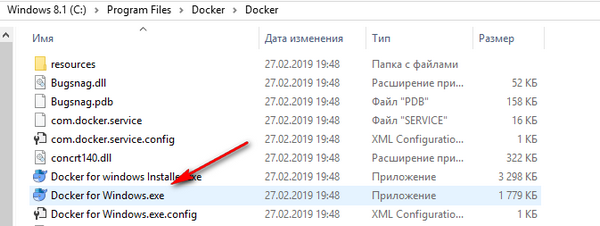
Navigate to the folder where you installed Docker and double click on the Docker for Windows.exe file.
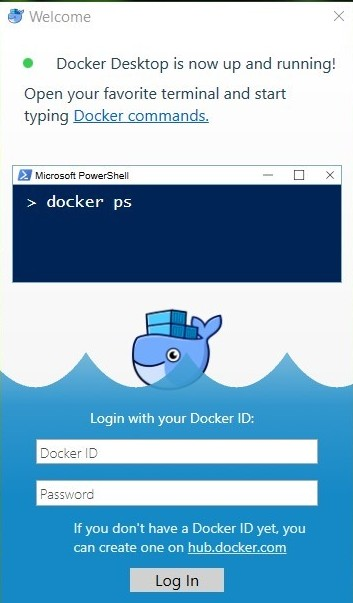
Soon you will see a pop-up window. Enter your credentials.
Pulling the container image¶
To run containers pull the container image:
docker pull registry.gitlab.com/librehealth/toolkit/lh-toolkit-docker:latest
You should see the similar console output:
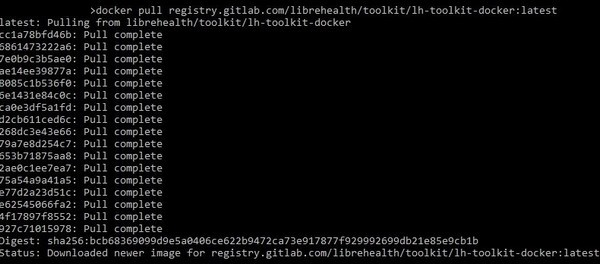
Navigate to the directory where you cloned this project. Depending on how you want to interact with the container, run it in foreground or as a daemon.
To run the container in the foreground:
docker-compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml up
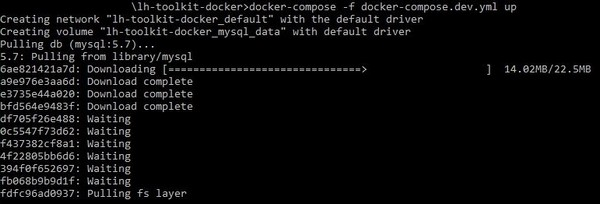
You may see a pop-up asking whether you want to share drive. Click Share it to continue.
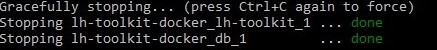
MySQL will be started first and then LH Toolkit will be started on the containers.
When you are done using LH Toolkit you can press Ctrl+C to stop the container. Do not do this unless you want to stop Docker.
To run the container in the background:
docker-compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml up -d
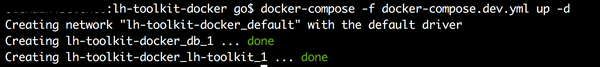
Using LH Toolkit¶
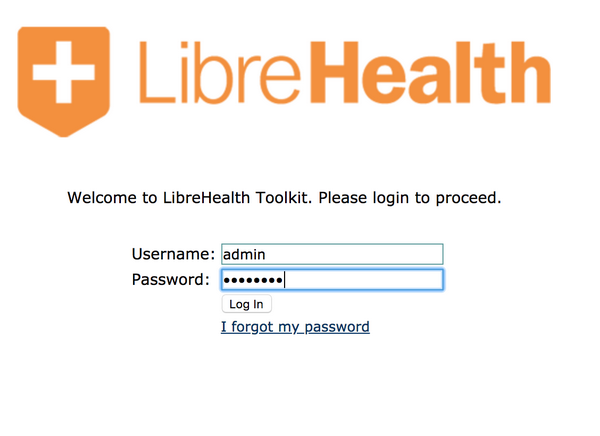
To start using LH Toolkit, point your browser to localhost:8080/lh-toolkit. The following are the authentication information:
User: admin
Pass: Admin123
Bringing container down¶
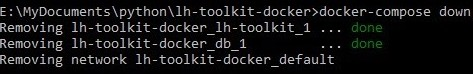
To bring the container down and to free space on your machine run:
docker-compose down
Troubleshooting¶
When you are pulling the container image, the directory you are in does not matter. However, if you try to run this docker image from outside of this project directory, you will get the following error:
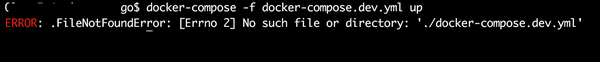
Navigate to the project directory and enter the command again.
If you try to pull an image before starting the Docker daemon, you will see an error:
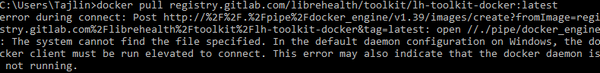
Navigate to the folder where you installed Docker and double click on the Docker for Windows.exe file.
You might see the following warning on the older systems:
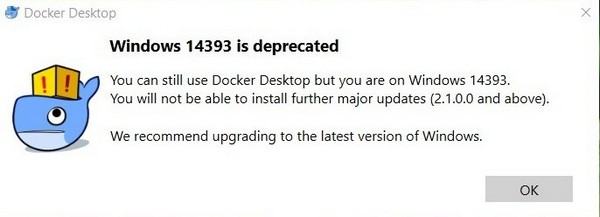
Ignore it or update your system.